
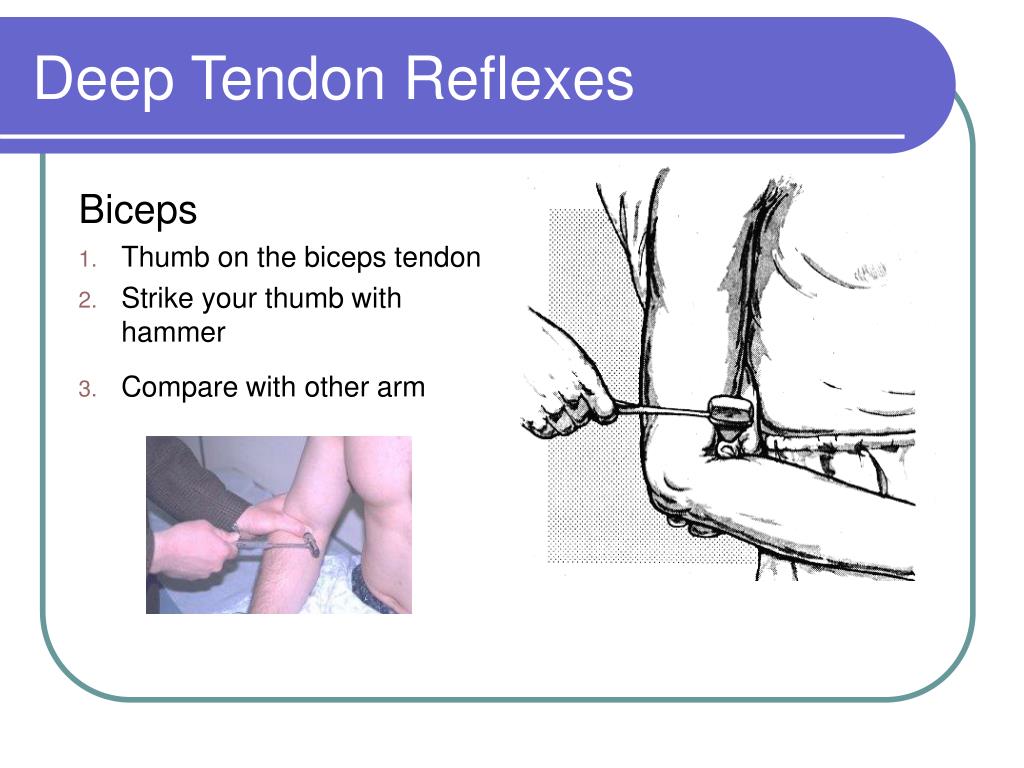
Ask the patient to relax their arm and allow it to fully be supported by your hand. Support the patient’s arm underneath their bicep to maintain a position midway between flexion and extension. The triceps reflex assesses cervical spine nerves C6 and C7. See Figure 6.37 for an image of obtaining the brachioradialis reflex.įigure 6.37 Brachioradialis Reflex Triceps Reflex The reflex consists of flexion and supination of the forearm.

Identify the insertion of the brachioradialis tendon on the radius and briskly tap it with the reflex hammer. Ask the patient to support their arm on their thigh or on your hand. The brachioradialis reflex is used to assess the cervical spine nerves C5 and C6. View Stanford Medicine’s Assessment of Deep Tendon Reflexes Video. To observe assessment of deep tendon reflexes, view the following video. 4+: Hyperactive with clonus (involuntary muscle contraction).Reflexes are graded from 0 to 4+, with “2+” considered normal: Before classifying a reflex as absent or weak, the test should be repeated after the patient is encouraged to relax because voluntary tensing of the muscles can prevent an involuntary reflexive action. Use a reflex hammer in a quick striking motion by the wrist on various tendons to produce an involuntary response. To perform deep reflex tendon testing, place the patient in a seated position. Spinal cord injuries, neuromuscular diseases, or diseases of the lower motor neuron tract can cause weak or absent reflexes. Assessment of reflexes is not typically performed by registered nurses as part of a routine nursing neurological assessment of adult patients, but it is used in nursing specialty units and in advanced practice.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
